What percentage of Individuals have Psoriasis(New Data)
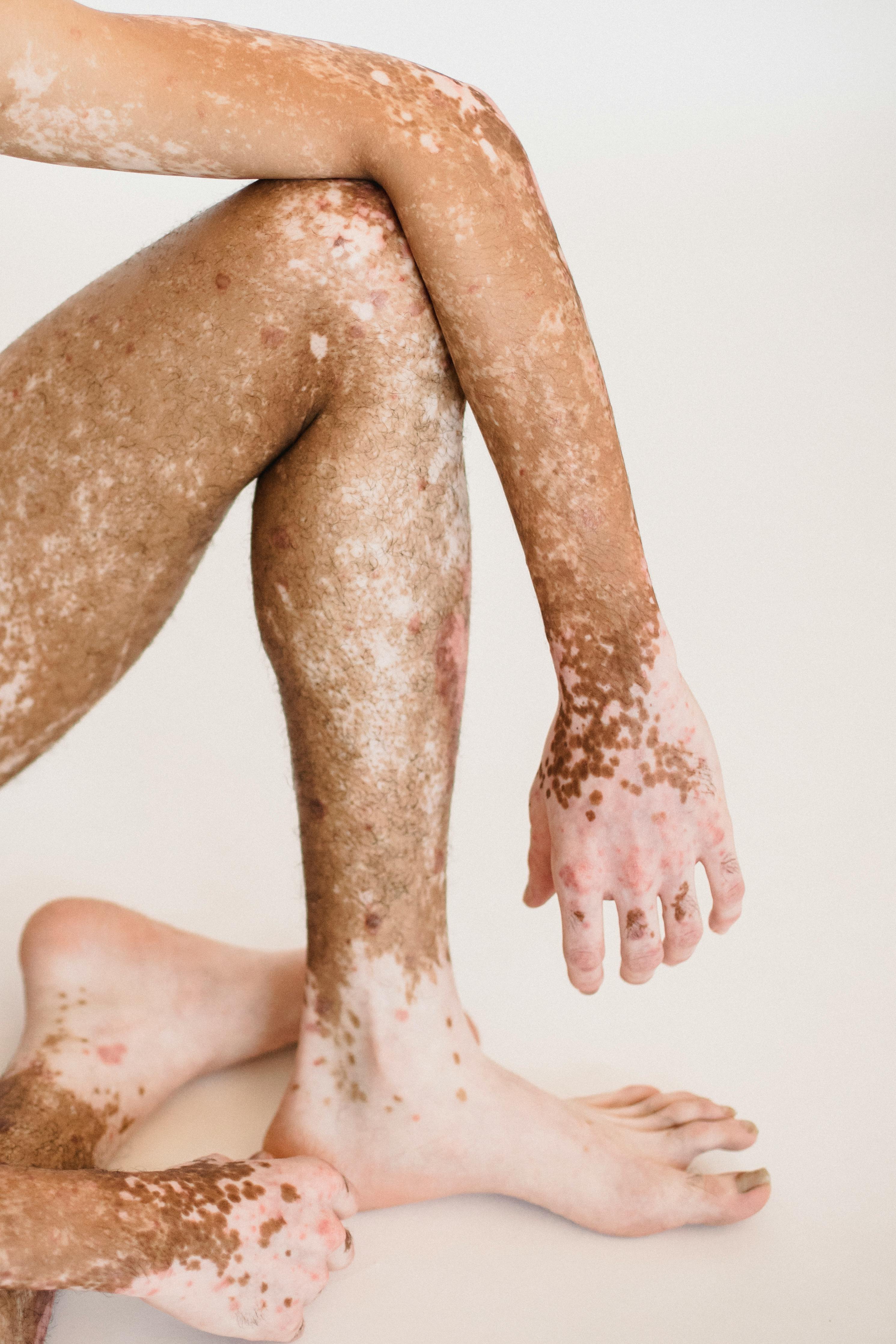

Psoriasis is a condition characterized by itchy and dry patches that appear on the skin. Interestingly, it can affect individuals at a young age, with up to 40% experiencing symptoms even before reaching the age of 16.
Surprisingly, 10% of those affected by psoriasis may develop this condition before they turn 10.
According to the National Psoriasis Foundation, over 8 million individuals in the United States are affected by psoriasis. Globally, approximately 2 to 3% of the world's population, which amounts to around 125 million people, live with this condition.
Although psoriasis is more common in adults, it can also affect children. Approximately 1 percent of children develop psoriasis.
Table of Contents
- Psoriasis Statistics - (Editor’s Choice)
- What is Psoriasis , and How Does it Affect Individuals?
- Where Is Psoriasis Most Common?
- How Many People Know About Psoriasis?
- The Need for Awareness
- What Can We Do?
- How Is Psoriasis Linked to Race and Ethnicity?
- What Factors Influence Psoriasis Statistics in the U.S.?
- Why is Early Detection and Intervention is Critical for Psoriasis?
- Challenges in Understanding and Addressing Psoriasis: What's Next?
- Final Thoughts
Psoriasis Statistics - (Editor’s Choice)
- Within the African American community, the prevalence is estimated to be around 2%. psoriasis is most likely to appear first between the ages of 15 and 35 years old.
- According to the International Federation of Psoriasis Associations (IFPA), nearly 3 percent of the world’s population has some form of psoriasis. That’s over 125 million people.
- The accuracy of data decreases for other ethnic groups due to imperfect sources; however, it is estimated to be approximately 1.2% in the Asian population.
- For individuals of Hispanic ethnicity and other groups, the prevalence is even lower, estimated to be around 0.5%. Please note that Hispanic is considered an ethnicity rather than a racial category in this context.
- This percentage corresponds to an estimated 7.55 million adults in the United States living with psoriasis, based on 2020 US census data.
- The prevalence of psoriasis is relatively similar between genders, with a rate of 3.2% in women and 2.8% in men.
- Among racial and ethnic groups, White individuals have the highest psoriasis prevalence at 3.6%, followed by other racial/ethnic groups (non-Hispanic, including multiracial) at 3.1%, Asian individuals at 2.5%, Hispanic individuals (including Mexican American and other Hispanic individuals) at 1.9%, and Black individuals at 1.5%.
- Psoriasis prevalence does not significantly differ based on patients' marital status, education level, income, or medical insurance status.
Sources : Pubmed, Wiley ScienceDirect
What is Psoriasis , and How Does it Affect Individuals?
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated condition, which means it's a disease with an unclear cause that leads to inflammation in the body due to issues with the immune system.
This inflammation can manifest as visible signs on the skin, including raised plaques and scales. It's important to note that the appearance of these plaques can vary depending on an individual's skin type.
The reason behind these skin changes lies in the overactivity of the immune system, which accelerates the growth of skin cells. Normally, skin cells go through a full cycle of growth and shedding over the course of a month.
However, in individuals with psoriasis, this process happens in just three or four days. Instead of shedding, the excess skin cells accumulate on the skin's surface, leading to the formation of plaques and scales.
For some people, these psoriasis plaques can be bothersome, causing itching, burning, and stinging sensations. These skin changes can occur on any part of the body but are commonly found on areas like the elbows, knees, and scalp.
Understanding and managing psoriasis is important for those affected by it, as it can impact both physical comfort and emotional well-being.
Sources : Pubmed, Wiley ScienceDirect
Where Is Psoriasis Most Common?
Psoriasis seems to be more prevalent in northern European countries, with Norway having the highest number of affected individuals, while East Asia tends to have the lowest rates.
The United States also experiences a relatively high prevalence of psoriasis. Furthermore, there are indications suggesting that the occurrence of psoriasis is increasing globally.
Related: Medical Errors Facts & Statistics in Healthcare
How Many People Know About Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a common yet often misunderstood skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it is prevalent, awareness about psoriasis remains relatively low compared to other medical conditions.
Despite being a widespread condition, psoriasis is sometimes referred to as a "hidden epidemic." Many people, even those not directly affected, may not know much about it. This lack of awareness can have several consequences:
- Stigma and Misconceptions: Due to the visible nature of psoriasis symptoms, individuals with the condition may experience stigma and misunderstanding. Others may wrongly believe that psoriasis is contagious or a result of poor hygiene.
- Delayed Diagnosis: Low awareness can lead to delayed diagnosis. Some individuals may live with psoriasis for years before receiving a proper diagnosis, which can hinder early intervention and effective treatment.
- Psychosocial Impact: Psoriasis can significantly impact a person's emotional well-being. Lack of understanding from friends, family, and the broader community can exacerbate feelings of embarrassment and isolation.
- Limited Support: Individuals with psoriasis may struggle to find the support they need because people around them are unaware of the challenges they face. Support systems, including healthcare providers and support groups, play a crucial role in managing the condition.
The Need for Awareness
Increasing awareness about psoriasis is vital for several reasons:
- Early Detection and Intervention: Knowledge about psoriasis can lead to earlier detection and treatment. Early intervention can prevent the progression of the condition and improve overall quality of life.
- Reducing Stigma: Raising awareness can help reduce the stigma associated with psoriasis. This, in turn, fosters a more compassionate and inclusive society for individuals living with the condition.
- Advocacy and Research: Greater awareness can drive advocacy efforts and support research into better treatments and a cure for psoriasis.
- Improving Support Systems: When more people understand psoriasis, it becomes easier to create support networks and resources for those affected.
- Empowering Individuals: Knowledge empowers individuals with psoriasis to seek help, manage their condition effectively, and advocate for their needs in healthcare settings.
Sources : Pubmed, Wiley ScienceDirect
What Can We Do?
Increasing awareness about psoriasis is a collective effort. Here are some steps we can take:
- Educate Ourselves: Learning about psoriasis and its impact is the first step in raising awareness. Reliable sources of information, including healthcare providers and reputable organizations, can provide accurate information.
- Start Conversations: Talk openly about psoriasis with friends, family, and colleagues. Share your knowledge and correct misconceptions when they arise.
- Support Psoriasis Organizations: Support organizations and initiatives dedicated to psoriasis awareness, research, and patient advocacy.
- Advocate for Equal Treatment: Advocate for equal treatment and understanding of individuals with psoriasis in all aspects of life, including employment and social interactions.
Increasing awareness about psoriasis is crucial for improving the lives of millions of people living with this condition. By fostering understanding and empathy, we can help individuals with psoriasis feel more supported and less isolated.
Together, we can make strides towards a more aware and compassionate society where everyone has the opportunity to live their best life, regardless of their skin condition.
How Is Psoriasis Linked to Race and Ethnicity?
In the United States, a higher proportion of white individuals receive diagnoses for psoriasis compared to people of color.
According to a 2021 study examining psoriasis rates among different racial and ethnic groups, the percentages of adults aged 20 and above diagnosed with psoriasis were 3.6% for white individuals, 2.5% for Asians, 1.9% for Hispanics, and 1.5% for Black individuals.
Researchers note that the prevalence of psoriasis in the U.S. has remained relatively stable since 2003.
While genetics may contribute to the higher occurrence of psoriasis in white populations, experts suggest that the condition might be more prevalent among people of color than existing research data indicate.
What Factors Influence Psoriasis Statistics in the U.S.?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people in the United States. It's essential to understand the factors that influence psoriasis statistics in the U.S., as this knowledge can help improve awareness, diagnosis, and treatment for those living with this condition.
- Genetics: One of the most significant factors in psoriasis statistics is genetics. Psoriasis tends to run in families, suggesting a hereditary component. If you have a family member with psoriasis, you may be at a higher risk of developing it yourself. Genetic factors can influence the age of onset, severity, and type of psoriasis an individual may experience.
- Immune System: Psoriasis is considered an immune-mediated disease. An overactive immune system can trigger the inflammation and rapid skin cell growth characteristic of psoriasis. Factors such as stress, infections, or other immune system-related conditions can exacerbate or trigger psoriasis flare-ups.
- Ethnicity and Race: Psoriasis prevalence varies among different racial and ethnic groups. Studies have shown that psoriasis is more common in individuals of European descent, with higher rates among White populations. However, it can affect people of all races and ethnicities.
- Lifestyle Factors: Lifestyle choices also play a role. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of psoriasis and may worsen the condition in those already affected. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help manage psoriasis symptoms.
- Environmental Triggers: Certain environmental factors can influence psoriasis. Cold weather, dry air, and sunburn can trigger or exacerbate flare-ups. Climate and geographical location can impact the prevalence of psoriasis in different regions of the U.S.
- Access to Healthcare: Socioeconomic factors can influence psoriasis statistics. Limited access to healthcare can result in underdiagnosis and undertreatment of psoriasis, particularly among marginalized communities. Efforts to improve access to medical care are essential in addressing this disparity.
- Advancements in Diagnosis: Improved diagnostic techniques and increased awareness among healthcare providers have led to better recognition of psoriasis cases. This has contributed to the rise in reported psoriasis cases over the years.
- Treatment Options: Advances in treatment options, including topical creams, oral medications, biologics, and phototherapy, have made it possible for more individuals to manage their psoriasis effectively. As treatment options expand, more people may seek medical help, contributing to the statistics.
Why is Early Detection and Intervention is Critical for Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While it may manifest as visible skin symptoms, its impact often goes far beyond the surface.
Early detection and intervention are paramount in effectively managing psoriasis and improving the quality of life for those affected. Here's why:
- Preventing Progression: Psoriasis tends to worsen over time if left untreated. Early detection allows healthcare professionals to intervene before the condition advances, reducing the severity of symptoms and potential complications.
- Enhancing Treatment Success: Timely diagnosis enables healthcare providers to initiate appropriate treatments promptly. The earlier treatment begins, the more likely it is to be effective in controlling symptoms and preventing flare-ups.
- Preventing Complications: Psoriasis is associated with several comorbidities, including psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome. Detecting psoriasis early allows for the management of these associated conditions, reducing the risk of complications.
- Improving Quality of Life: Psoriasis can have a profound impact on a person's physical and emotional well-being. Early intervention can alleviate discomfort, reduce the risk of disability, and help individuals lead a more fulfilling life.
- Psychosocial Support: Psoriasis is not just a skin condition; it affects a person's self-esteem and mental health. Detecting psoriasis early provides an opportunity for healthcare providers to offer psychosocial support, which can be crucial in addressing the emotional toll of the condition.
- Preventing Disability: Psoriatic arthritis, a common complication of psoriasis, can lead to joint damage and disability if not managed early. Identifying and treating psoriatic arthritis in its initial stages can help prevent long-term disability.
- Personalized Treatment: Early detection allows for a more tailored treatment approach. Healthcare providers can work with individuals to find the most suitable treatment options based on their specific needs and preferences.
- Reducing Healthcare Costs: Timely intervention can prevent the need for more intensive and costly treatments down the line. It can also reduce the economic burden on individuals and healthcare systems.
- Promoting Awareness: Early detection efforts contribute to increased awareness of psoriasis, which, in turn, reduces stigma and encourages people to seek help sooner.
- Better Long-Term Outcomes: Early intervention not only improves short-term symptom management but also leads to better long-term outcomes. It can reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups, allowing individuals to enjoy a better quality of life.
Challenges in Understanding and Addressing Psoriasis: What's Next?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing discomfort, pain, and sometimes even emotional distress. While significant progress has been made in the understanding and management of psoriasis, several challenges persist.
- Complex Causes: The exact cause of psoriasis remains elusive. It's believed to be a complex interplay of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Researchers are continuously striving to unravel these complexities to develop more targeted treatments.
- Varied Presentations: Psoriasis doesn't manifest the same way in everyone. There are different types of psoriasis, each with its unique characteristics. This heterogeneity makes diagnosis and treatment a nuanced process, requiring personalized care.
- Psychosocial Impact: Psoriasis isn't just skin deep; it can profoundly affect a person's emotional well-being. The visible nature of the condition can lead to feelings of self-consciousness, anxiety, and depression. Addressing the psychosocial impact of psoriasis is a crucial aspect of holistic care.
- Limited Awareness: Despite its prevalence, psoriasis still lacks widespread awareness. Many people may not recognize the symptoms or understand the challenges faced by those with psoriasis. Raising awareness is essential to reduce stigma and promote early diagnosis.
- Access to Treatment: Access to effective psoriasis treatments can be challenging, especially for underserved populations. The cost of medications and limited access to dermatologists can be barriers to receiving proper care. Addressing these disparities is crucial for equitable healthcare.
- Treatment Response Variability: Not all treatments work the same for every individual with psoriasis. Some may respond well to one medication, while others may require a different approach. Predicting treatment response and tailoring therapies accordingly is an ongoing challenge.
- Research Gaps: While there have been significant advancements in psoriasis research, there are still gaps in our understanding. More research is needed to explore potential triggers, long-term outcomes, and the link between psoriasis and other health conditions.
- Holistic Care: Managing psoriasis involves more than just treating the skin symptoms. It's essential to address comorbidities, promote a healthy lifestyle, and provide emotional support. A holistic approach to care can improve the overall well-being of individuals with psoriasis.
So, what's next for psoriasis? The future looks promising. Ongoing research aims to uncover the precise mechanisms behind psoriasis and develop more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Advances in personalized medicine may lead to tailored therapies for individual patients, increasing treatment success rates.
Additionally, efforts to raise awareness and reduce stigma are gaining momentum. Patient advocacy groups, healthcare professionals, and individuals with psoriasis are working together to shed light on this condition and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Sources : Pubmed, Wiley ScienceDirect
Final Thoughts
In understanding the factors that influence psoriasis statistics in the U.S. is vital for healthcare professionals, policymakers, and individuals affected by psoriasis.
By addressing genetic, immune, lifestyle, and environmental factors, as well as disparities in access to healthcare, we can work towards better management and support for those living with this chronic skin condition.
Increased awareness, research, and access to effective treatments can improve the quality of life for individuals dealing with psoriasis.